
The tensor muscle of the soft palate (TVP) not only functions to open up the lumen of the Eustachian tube, but it also contributes to mastication as it is actively involved in the process of phonation, swallowing, chewing. There are 6 muscles recognized as having an active role in the functions of the tube: tensor tympani, salpingopharyngeus tensor veli palatini levator veli palatini lateral and medial pterygoids. The discontinuous opening of the pharyngeal ostium in the nasopharynx causes peristaltic-like movements that may be due to the visco-elastic features of the tubular structure of the cartilage. It then proceeds forward, downward, and medially, to form a 45-degree angle to the sagittal plane, and about a 30-degree angle to the horizontal plane. The Eustachian tube is located in the para-pharyngeal space and is closely linked to the infratemporal fossa. The Eustachian tube continues from the front wall of the middle ear to the sidewall of the nasopharynx, progressing along the posterior edge of the medial pterygoid plate. The active opening of the Eustachian tube to relieve positive or negative pressure in the middle ear commonly is called “clearing the ear.” These can be actively pulled apart to open the tube with the help of accessory muscles or passively pushed apart by air exiting or entering the middle ear under pressure. Partly a hollow tube in bone and partly a potential space in fibroelastic cartilage, the Eustachian tube is normally closed, as its proximal walls are collapsed. Patency of the tube allows for air exchange in the tympanic cavity to replenish oxygen to the middle ear, in addition to providing an outlet for mucus and other fluid from the middle ear. It is believed that the Eustachian tube also may be involved in sound transformation through reverberation phenomena.
It thus influences the tension in this structure and the attached ossicles, and in this way indirectly affects the effectiveness of sound wave transmission.

In doing so, the Eustachian tube allows for regulation of the pressure across the tympanic membrane. More specifically, the Eustachian tube permits equalization of pressure in the middle ear with respect to ambient pressure. There is a huge need for this procedure, and it will greatly reduce the need for all those ear tubes” and other related surgeries.The Eustachian tube plays a role in equalization, oxygenation, and drainage of the tympanic cavity in the middle ear. “Every time the tubes come out, they need the tubes in again. “There are people who need tubes 13 or 14 times,” he said. Still, Kaylie believes it will be a significant advance for millions of people who require ear tube surgery.
#Auditory tube trial#
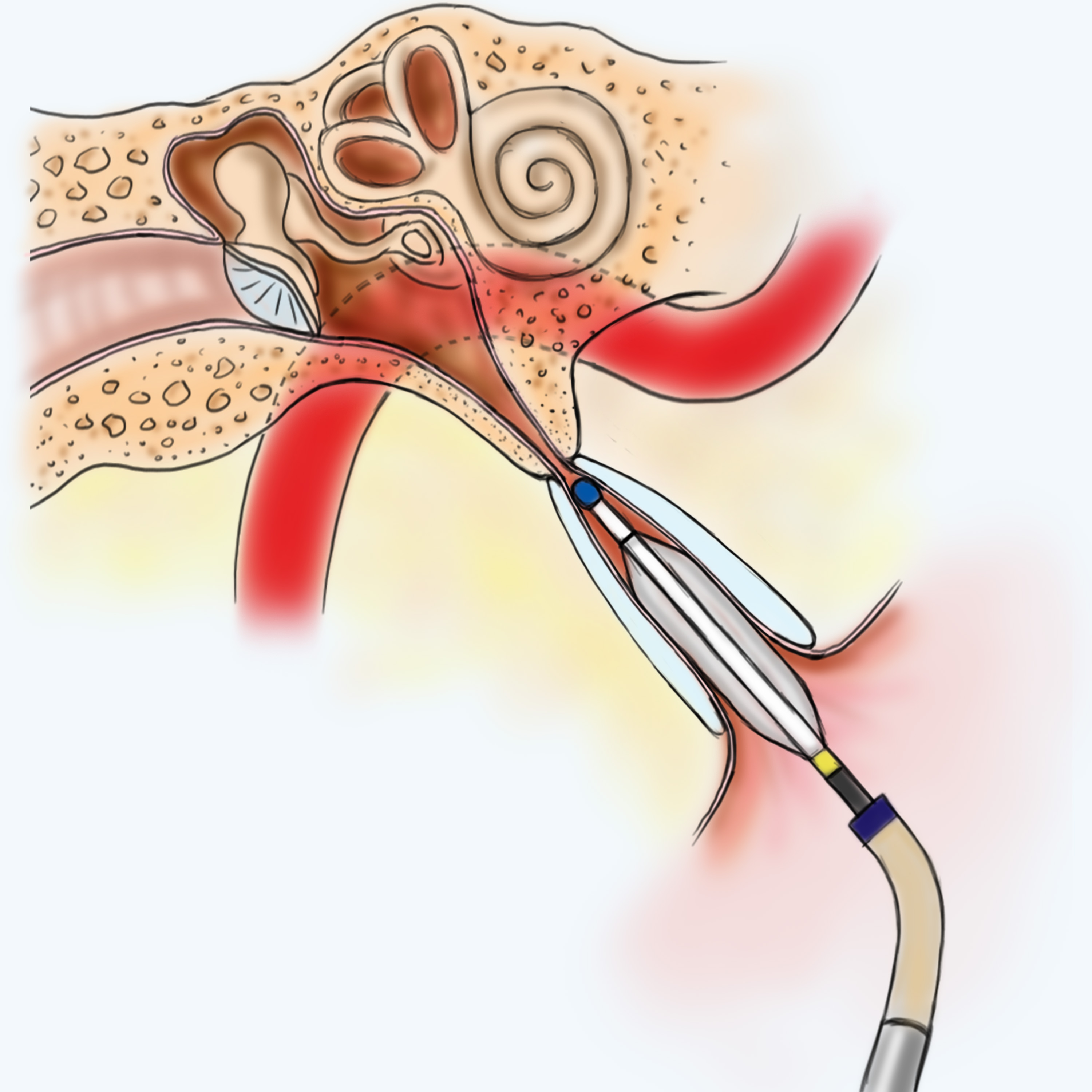
During the clinical trial for the Aera system, some common problems included small tears in the lining of the eustachian tube, minor bleeding, and sometimes, worsening of their eustachian tube dysfunction. While Kaylie believes the device will prove useful to many people who currently require ear tube surgery due to eustachian tube dysfunction, fluid in their ears, or chronic ear infections, he also cautions that there are some people for whom it will not be appropriate. Once the tube is open, the balloon is deflated and removed. The balloon is inflated, which opens the eustachian tube and allows air to flow through. Studies of the device showed “long-term normal eustachian function after the procedure.”ĭuring the minimally invasive procedure, a catheter is used to insert a small balloon through the nose and into the eustachian tube. “This new device has been shown to return the middle ear to normal and greatly eliminate middle ear pressure in properly selected patients,” he said. With the FDA-approved Aera system, children and adults with chronic eustachian tube dysfunction can opt for a simple, 10-minute procedure instead, Kaylie said. Recurrent eustachian tube dysfunction requires the surgical placement of tubes in the eardrum, which allows pressure to equalize in the middle ear. Stuffy ears and noses, hearing loss, ear pain and pressure, as well as ringing in the ears (tinnitus) can result.īlocked eustachian tubes can be relieved by nasal sprays and antihistamine tablets, which reduce inflammation and congestion. When the tube is blocked from a cold, sinus or nose problems, or ear infections, air can no longer pass through. “This allows you to equalize pressure” on either side of the eardrum, explained David Kaylie, MD, a Duke otolaryngologist. Normally, the tube is filled with air and opens when yawning or chewing. The eustachian tube is the main connection between the back of the throat and the middle of the ear.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
